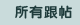
2023-4-14
珍珠瓷是英國瓷器大家韋基伍德於1779年首先發明並使用的,是一種中溫釉下青花或釉下五彩陶器,以黃藍綠叄種顏色為主,在白胎瓷土上面的氧化鉛瓷釉里添加了少量的化學物氧化鈷藍,使得燒成的白地陶器的釉面,呈一絲澹澹的藍,這就更加接近中國早期外銷瓷器上的玻璃釉,因此又叫中國釉,珍珠白和珍珠瓷釉。其他廠家,都是從威基伍德哪兒學來的。

Pearlware is an earthenware made by Josiah Wedgwood in 1779. It was copied by other potters in England. Pearlware is only slightly different in color from creamware and for many years collectors have confused the terms. Only certain colors like blue, yellow, and green were used as underglaze paintings for pearlware because materials for other colors could not stand the heat necessary to fire the glaze.
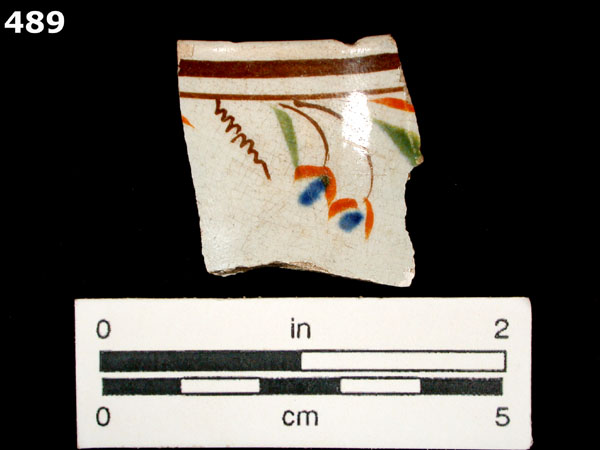
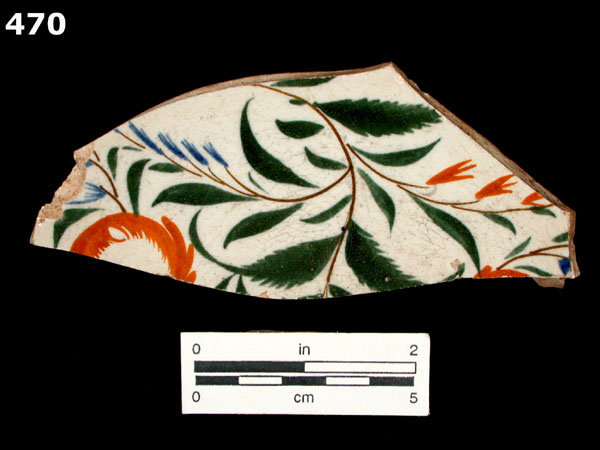
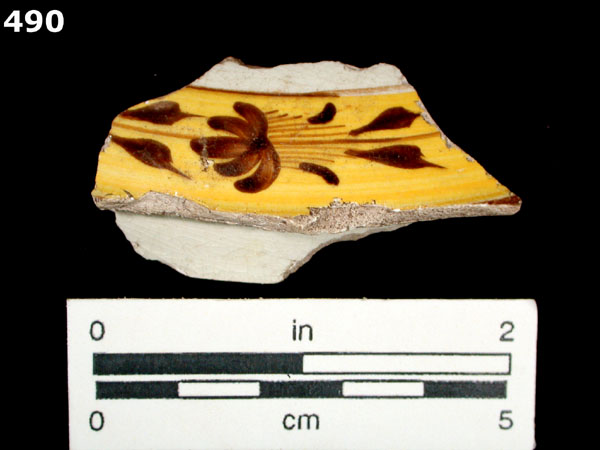
This style of polychrome hand-painted refined earthenware is also known as Gaudy Dutch. It can occur on a background of pearlware or creamware, however, the dates are currently thought to be the same for both.
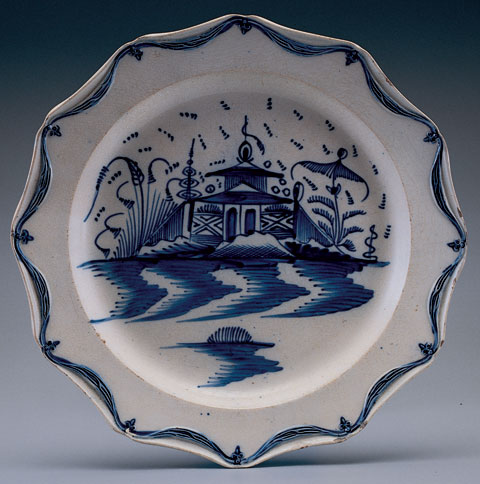
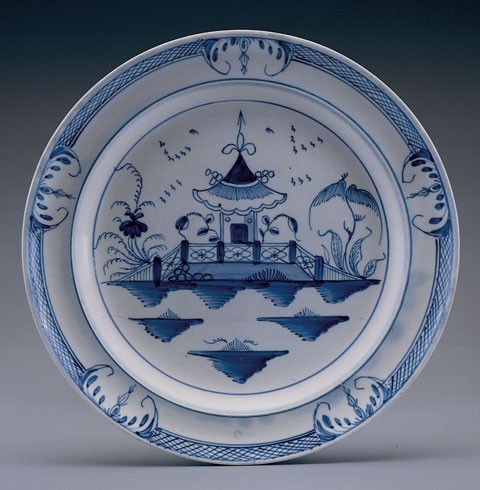
White to light cream-colored, thin, hard, refined earthenware paste. White to faint bluish-white clear lead glazed background, caused by the addition of cobalt to the glaze. There is a bluish cast where the glaze pools. Delicately painted floral wreath designs in olive green, brown, blue, and mustard yellow. If the motif occurs on creamware, the background is pale creamy yellow. We usually refer to any ceramics with the blue-tinted glaze as pearlware, an adaptation of Wedgwood’s pearl white, but some may refer to pearlware with a Chinese-style decoration as China glaze.
顧名思義,奶黃瓷釉微微發黃,也是威基伍德發明的,可是存在的時間更早一些,在1765年前後,是在以氧化鉛為主的釉水中加入了氧化銅才產生的。等到珍珠瓷釉發明並進入正規生產之後,奶黃白瓷釉就澹出了市場。
左邊是奶黃釉,右邊是珍珠白釉,又稱中國釉。
Creamware, the earliest of the three, was formally introduced in England by Josiah Wedgwood in 1762. Cream-colored wares were being produced as early as the 1740s, but Wedgwood succeeded in creating a more refined ware. Wedgwood coined this ware as Queen’s Ware after completing his commission for Queen Charlotte in 1765 (Wedgwood Museum 2016). The creamy color seen in the glaze is achieved by the addition of copper to a lead oxide glaze. In places where the glaze pools, such as a footring, the glaze will look almost green. The popularity of creamware began to decline around 1800 with the introduction of pearlware and is virtually non-existent after 1820.
按理說奶黃釉和珍珠白釉,都是可憐的英國人為了在瓷器生產上彎道超車而多走了的彎路,不像那聰明的德國人,利用了工業間諜盜取了景德鎮的瓷器配方而一步到位,後來發現瓷釉中添加氧化鈷,一是需要增加成本,得不償失,二是發現鈷礦中,含有大量的氧化砷雜質也就是毒藥砒霜,會引發採礦工人和制瓷工人的職業病。於是才改邪歸正,直接燒制白瓷。
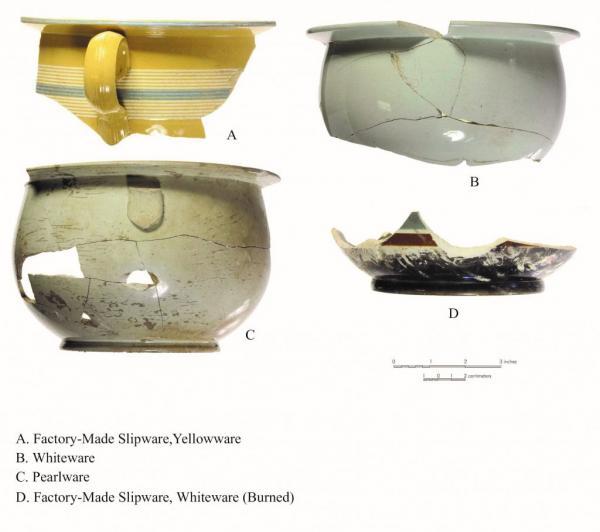
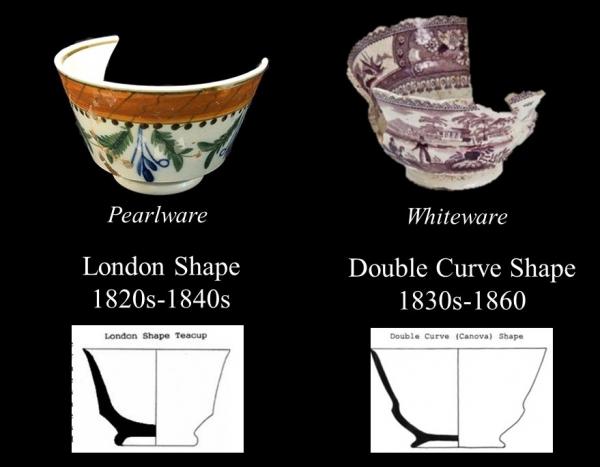
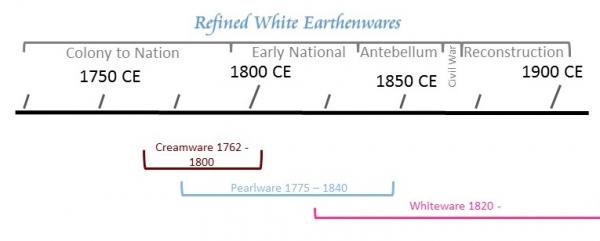
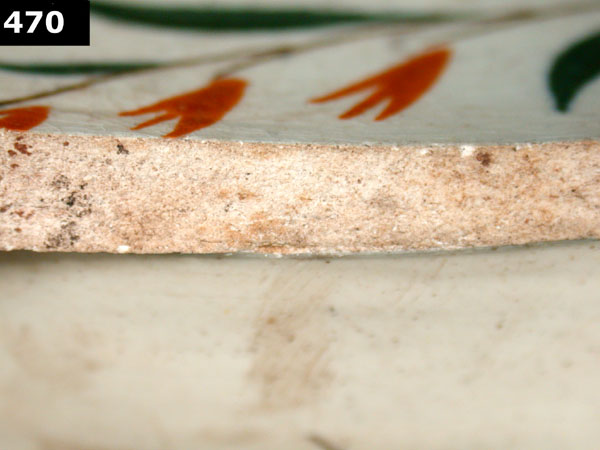
Over time the use of cobalt decreased, most likely due to the expense of obtaining the mineral. Fun fact: the word cobalt is derived from the German word kobalt, which means goblin. Cobalt ore, when smelted, produces a powder that contains arsenic, which is highly toxic. By around 1808 a fully whitened version of creamware (known as White Ware) was introduced to meet changing market demand. As the use of cobalt decreased, whiteware begins to emerge, approximately around 1820. During the transition between pearlware and whiteware, it can sometimes be difficult to determine the difference between the two. Early whitewares can have a slightly blue hue to the glaze, particularly in areas where the glaze is thicker. Sometimes we define this as transitional whiteware.
失去了顏色釉的瓷器,就回復到了梅森瓷器的高冷和一枝獨秀,也失去了瓷器的地方特色、多元化和競爭力。於是乎,進入二十世紀之後,曾經不可一世,興盛了兩百五十多年的英格蘭瓷器製造,也已經日薄西山,紛紛倒閉,關門大吉了。
|